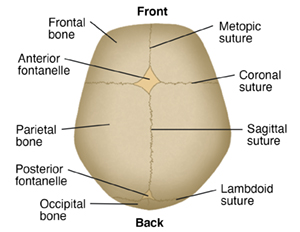
The skull may seem to be one large bone, but it's made of several major bones that are connected together. The major bones that compose the skull include:
-
2 frontal bones
-
2 parietal bones
-
1 occipital bone
These bony plates cover the brain, and are held together by fibrous material called sutures.
What are sutures?
Sutures allow the bones to move during the birth process. They act like an expansion joint. This allows the bone to enlarge evenly as the brain grows and the skull expands. The result is a symmetrically shaped head. Some sutures extend to the forehead, while others extend to the sides and back of the skull. One suture in the middle of the skull extends from the front of the head to the back. The major sutures of the skull include:
-
Metopic suture. This extends from the top of the head down the middle of the forehead, toward the nose. The 2 frontal bone plates meet at the metopic suture.
-
Coronal suture. This extends from ear to ear. Each frontal bone plate meets with a parietal bone plate at the coronal suture.
-
Sagittal suture. This extends from the front of the head to the back, down the middle of the top of the head. The 2 parietal bone plates meet at the sagittal suture.
-
Lambdoid suture. This extends across the back of the head. Each parietal bone plate meets the occipital bone plate at the lambdoid suture.
If any of the sutures close too early (fuse prematurely), there may be no growth in that area. This may force growth to happen in another area or direction. This results in an abnormal head shape (craniosynostosis).
What are fontanelles?
A fontanelle is the space between the bones of a baby's skull where the sutures intersect. There are 2 fontanelles. These spaces are covered by tough membranes (dura) that protect the underlying soft tissues and brain. The fontanelles include:
-
Anterior fontanelle (also called soft spot). This is the junction where the 2 frontal and 2 parietal bones meet. The anterior fontanelle remains soft until about 18 months to 2 years of age. Healthcare providers can assess if there is increased intracranial pressure by feeling the anterior fontanelle.
-
Posterior fontanelle. This is the junction of the 2 parietal bones and the occipital bone. The posterior fontanelle usually closes first, before the anterior fontanelle, during the first several months of an infant's life.
Because the fontanelles are soft early in life, it is easy to take pictures of a baby's brain with ultrasound.
Featured in